In modern day farming energy is introduced to a system via feeding, heat and artificial light; this increase in input makes for an increase in out put, a higher yield.
Productivity is the amount of chemical energy that plants make by photosynthesis. The net is calculated by the amount of energy produced from photosynthesis take away the amount that is used by the plant during respiration.
Net productivity= gross production - respiratory loss
In modern day farming farmers use any means possible to increase their yield, and therefore increase their profit.
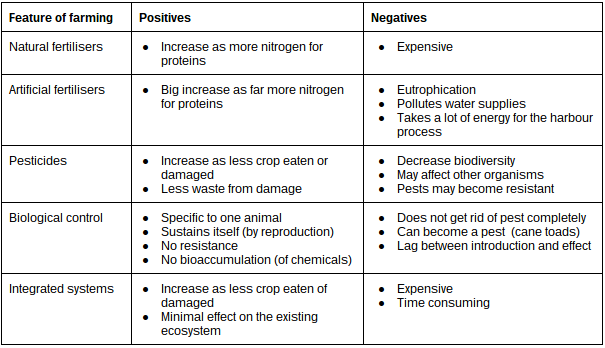
Natural fertilisers include manure and animal bone; things that naturally contain nitrogen. Artificial fertilizers contain nitrogen made by the harbour process and extracted from rocks.
Pesticides are chemicals that are spread on crops to kill pests (things that are eating or damaging crops). Biological control is the introduction of an organism that will eat a pest. An integrated system is a series of techniques used to try and keep pest damage to a minimum, without disturbing the biodiversity of an area e.g. choosing areas with few pests, encouraging natural predators to be around, removing but not killing pests.
Intensive farming also happens with livestock.
1 Slaughtered when still growing/before maturity/while young
so more energy transferred to biomass/tissue/production;
2 Fed on concentrate /controlled diet /controlled
conditions/so higher proportion of (digested) food
absorbed/lower proportion lost in faeces / valid reason for
addition;
3 Movement restricted so less respiratory loss / less energy
used;
4 Kept inside/heating/shelter / confined so less heat loss / no
predators;
5 Genetically selected for high productivity;

No comments:
Post a Comment